As 2025 comes to a close, now may be the ideal time to review your tax strategy and find potential opportunities. The steps you take before the end of the year might help you reduce your tax bill. Here are some ideas to consider.
Save now, have more later: If you’re participating in an employer-sponsored 401(k) or 403(b) plan, think about contributing the full pre-tax amount allowed to your retirement accounts by the end of the year. For 2025, the annual limit is $23,500 ($31,000 if you’re age 50 to 59 or 64 and older; $34,750 if you turn age 60, 61, 62, or 63 during the year). If you have a traditional or Roth IRA, you can contribute up to $7,000 for 2025, $8,000 if you’re age 50 or older.1 Traditional IRA contributions may be deductible, but Roth contributions are not.
Time it right, defer or accelerate income: If you expect a significant change in your income from one year to the next — for example, due to a bonus or investment gains — consider deferring or accelerating income. If you expect to be in a lower tax bracket next year, you may benefit from deferring some income into 2026 when it may be taxed at a lower rate. But, if you expect to be in a higher tax bracket next year, accelerating income in 2025 may help reduce your tax liability by taking advantage of your current rate. Timing matters when you’re close to a threshold that impacts tax rates, credits, or deductions.
Hold on for better rates: Holding your investments longer may help reduce your tax bill. If you have stocks or other assets that have appreciated in value, keeping the asset for more than a year means you are typically subject to long-term rates of 0%, 15%, or 20% on any capital gains from a sale (based on your income tax bracket). If you sell the asset earlier than this, your gains are generally taxed at ordinary income tax rates, which may be higher.
Harvest your losses: If you experience capital losses on securities and no longer want to hold the securities in your portfolio, consider selling these underperformers to offset gains from other investments. Losses above the amount of your gains can offset up to $3,000 of ordinary income ($1,500 if your filing status is married filing separately). Unused losses can be carried forward to future years. Watch out for the wash-sale rule, which precludes taking a capital loss deduction if you repurchase the same investment within 30 days before or after selling it.
Save today for your future health costs: Whether you have a health savings account (HSA) through your employer or one you’ve opened individually, contributing more now can help reduce your tax bill. You can boost your HSA savings by increasing payroll deductions or by making direct contributions to your account. For 2025, the contribution limits are $4,300 for individual coverage and $8,550 for family coverage (contributions made by you and your employer count toward this limit). Contributions made through payroll deductions help reduce your taxable income, and contributions made outside of payroll deductions are tax deductible.2
Give more, pay less: If you itemize deductions on your federal income tax return, you can generally deduct charitable contributions, but the deduction is limited to 50% (60% for cash contributions to public charities), 30%, or 20% of your adjusted gross income, depending on the type of property you give and the type of organization to which you contribute. Excess amounts can be carried over for up to five years.
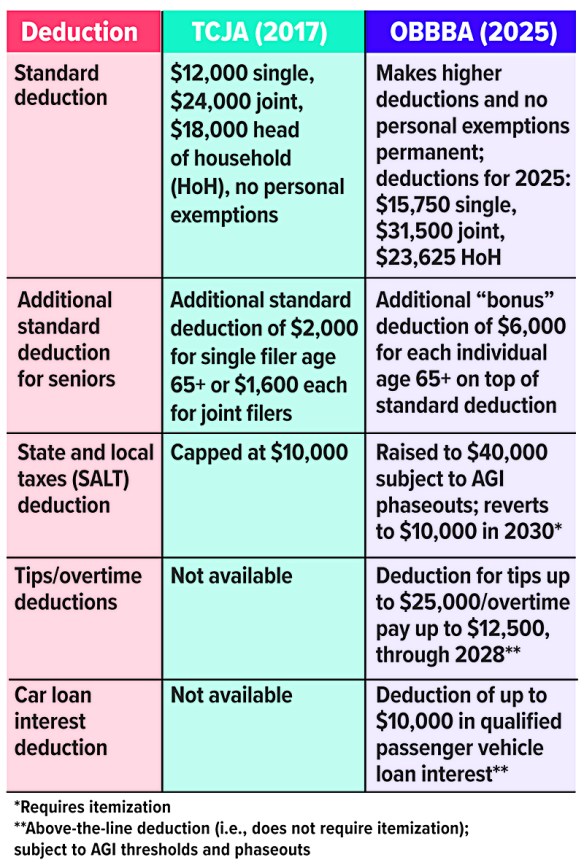
New Deductions
This chart compares some major deductions from the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) with updates in the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA), signed into law on July 4, 2025, and effective for the 2025 tax year.
Questions about this topic? Contact First Financial’s Investment & Retirement Center by calling 732.312.1534. You can also email mary.laferriere@lpl.com or maureen.mcgreevy@lpl.com
Securities and advisory services are offered through LPL Financial (LPL), a registered investment advisor and broker/dealer (member FINRA/SIPC). Insurance products are offered through LPL or its licensed affiliates. First Financial Federal Credit Union (FFFCU) and First Financial Investment & Retirement Center are not registered as a broker/dealer or investment advisor. Registered representatives of LPL offer products and services using First Financial Investment & Retirement Center, and may also be employees of FFFCU. These products and services are being offered through LPL or its affiliates, which are separate entities from and not affiliates of FFFCU or First Financial Investment & Retirement Center.
Securities and insurance offered through LPL or its affiliates are:
The information provided is not intended to be a substitute for specific individualized tax planning or legal advice. We suggest that you consult with a qualified tax or legal professional. LPL Financial Representatives offer access to Trust Services through The Private Trust Company N.A., an affiliate of LPL Financial. Content in this material is for general information only and not intended to provide specific advice or recommendations for any individual. All performance referenced is historical and is no guarantee of future results. All indices are unmanaged and may not be invested into directly. CRPC conferred by College for Financial Planning. This communication is strictly intended for individuals residing in the state(s) of CT, DE, FL, GA, MA, NJ, NY, NC, OR, PA, SC, TN and VA. No offers may be made or accepted from any resident outside the specific states referenced.
1–2) 2025 IRA and HSA contributions can be made up to April 15, 2026.
Prepared by Broadridge Advisor Solutions Copyright 2025.